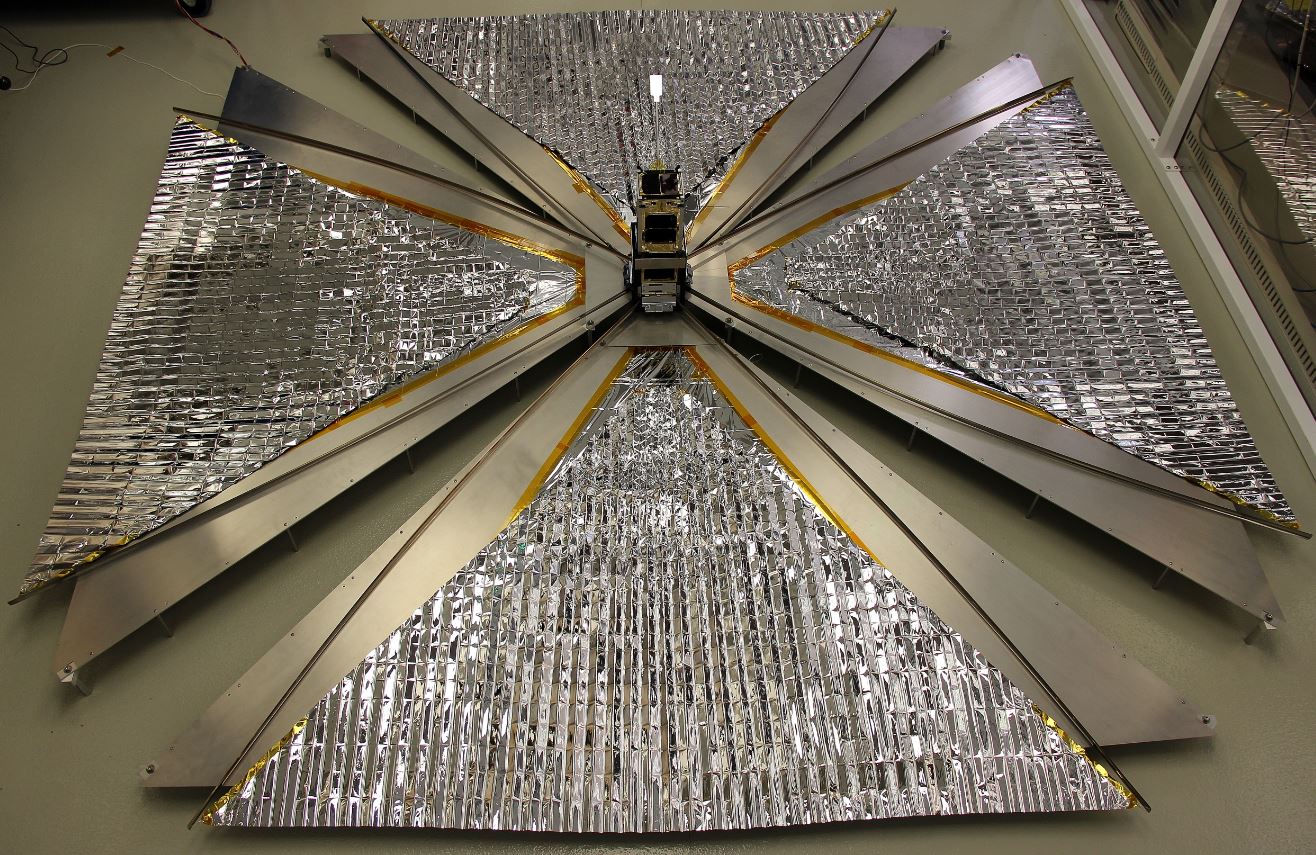
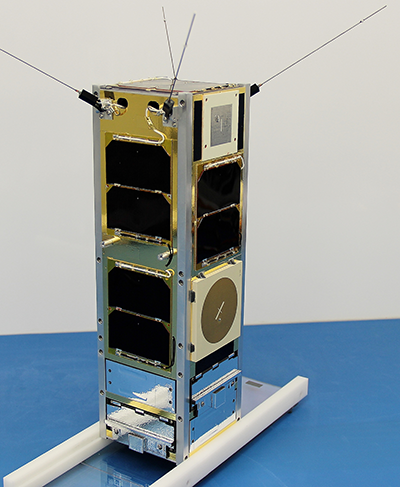
On 26 September 2016, an RMC Physics and Space Science payload was launched into low Earth orbit onboard the CanX-7 nanosatellite (10 × 10 × 34 cm, 3.5 kg). The payload demonstrated the feasibility of space-based monitoring of air traffic through the reception Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) signals. The satellite also carried a 4 m2 drag sail for accelerated de-orbiting to reduce space debris. CanX-7 detected ADS-B signals for seven months at which point the drag sail was deployed. On 21 April 2022, after approximately 30,000 revolutions of the Earth, CanX-7 has intentionally burned up on descent into the atmosphere. Both the ADS-B mission and drag sail operation were a great success!


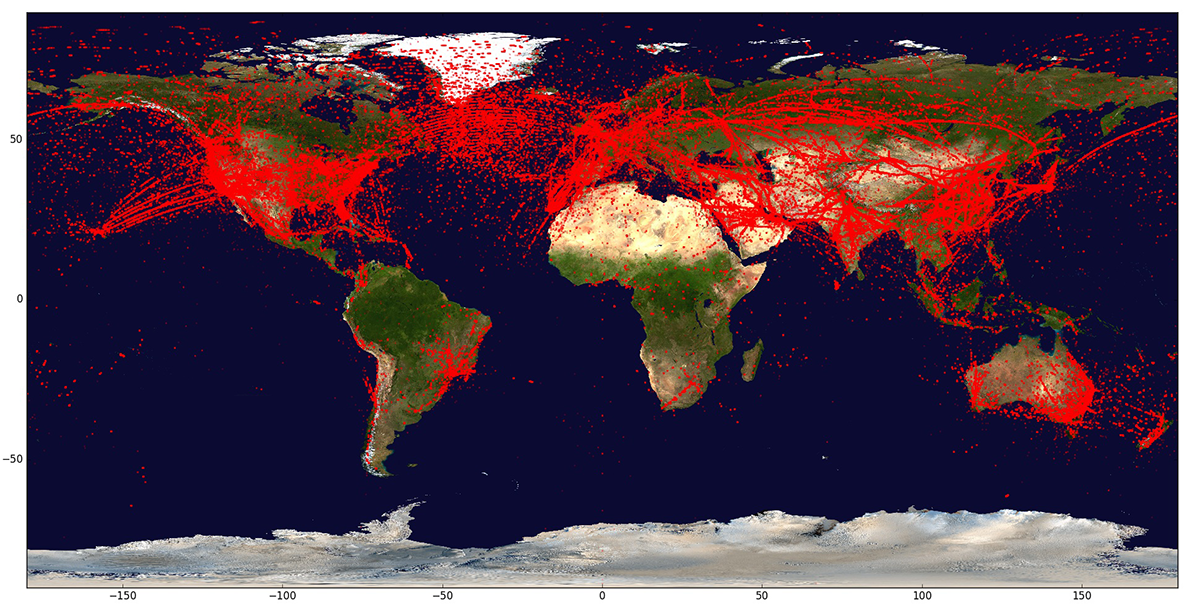
For more information, see The CanX-7 ADS-B Mission: Signal Propagation Assessment