Chef de département de physique et de sciences spatiales
Dr Lévesque est un membre du corps professoral depuis juillet 2005.
Ces activités de recherche sont reliées à l'optique infrarouge. Voici les sujets d'intérêt de ces activités de recherche. Chaque sujet d'intérêt est ensuite subdivisé dans un domaine plus spécifique.
1. Interaction laser-matière
1a. Spectroscopie des matériaux dans le proche et mi-infrarouge
Le rayonnement infrarouge est appliqué pour la caractérisation des matériaux à la spectroscopie à distance (1 km). Des signatures provenant d’un matériau donné sont utiles et l’information obtenue permet d’identifier le matériau ciblé à longue distance.
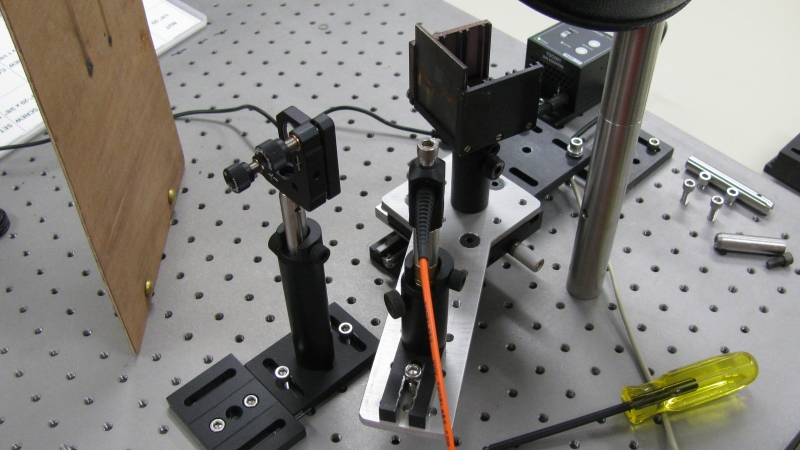
Par exemple, les figures 1 et 2 montrent les signatures spectroscopiques de deux types de verre différents. Plus d’analyses surplus de matériaux sont en cours dans les laboratoires afin de développer davantage la spectroscopie à distance. La figure 3 démontre comment les échantillons sont montés lors des analyses.
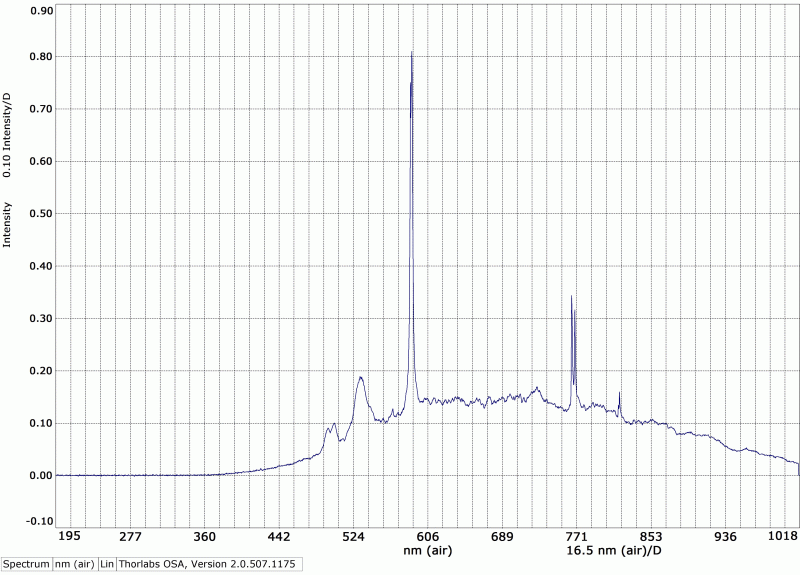
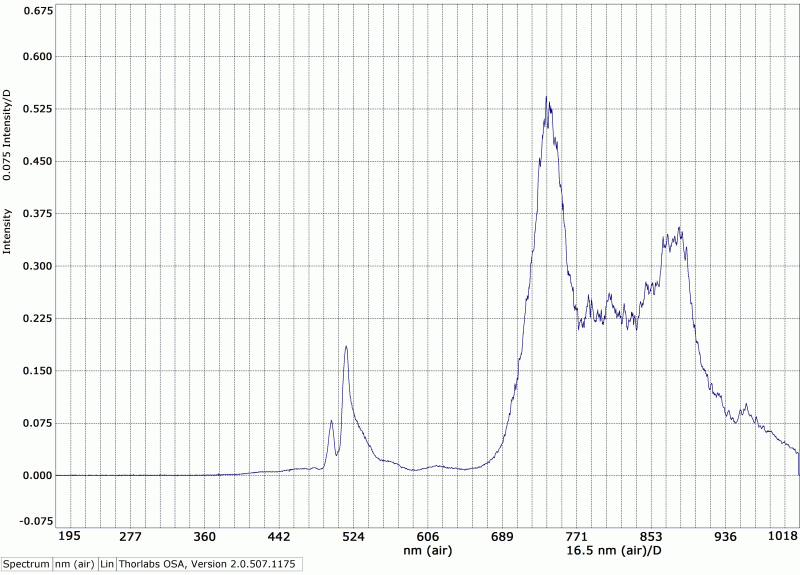
1b. Chauffage contrôlé à température constante par laser infrarouge
Le chauffage d’une solution aqueuse ou simplement d’un os peut favoriser la guérison lors d’application médicale telle l’ostéoporose ou la fabrication d’implants.
Maintenir le tissue biologique ou la surface des os peut aussi accélérer le traitement par la méthode (PDT). La figure 4 montre comment l’eau (5 ml) atteint une température constante sans trop de fluctuations thermiques pendant une période de 2 minutes.
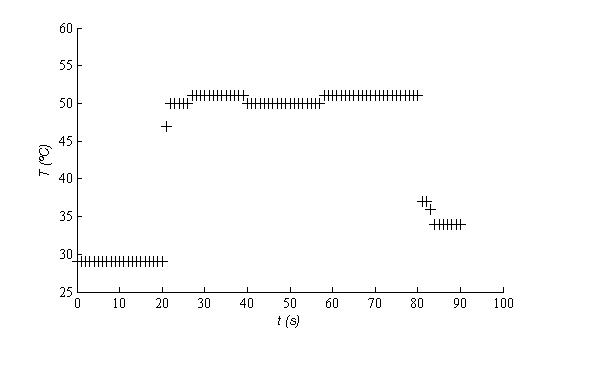
1c. Contrôle de la temperature par autocorrection avec lasers infrarouges
Des méthodes sont à l’essai pour mieux contrôler la température par des méthodes asservies en temps réel. Ce type de méthodes est souhaitable afin de réduire les fluctuations de la température (voir figure 4).
2. Micro-usinage de fibres par laser CO2.
2a. Fibre optic platforms structures
Le micro-usinage de petits trous (~50-60 µm) dans le cœur d’une fibre optique conventionnelle permet de contenir une substance fluorescente à analyser. Puisque les fibres se couplent bien à plusieurs instruments tels des spectromètres, on favorise souvent les fibres optiques comme plateforme d’essais.
2b. Surface nanoscale axial photonics (SNAP)
Les trouvailles sur les fibres conventionnelles ouvrent certaines portes sur des fibres ayant des effets de résonnance prononcées comme dans les fibres structures (SNAP). De telles fibres structures peuvent se fabriquer en faisant tourner la fibre autour de son axe en faisant fondre sa gaine localement.
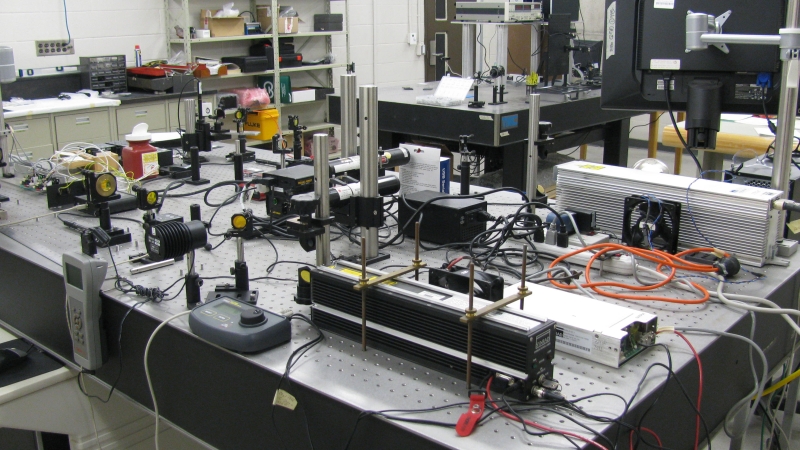
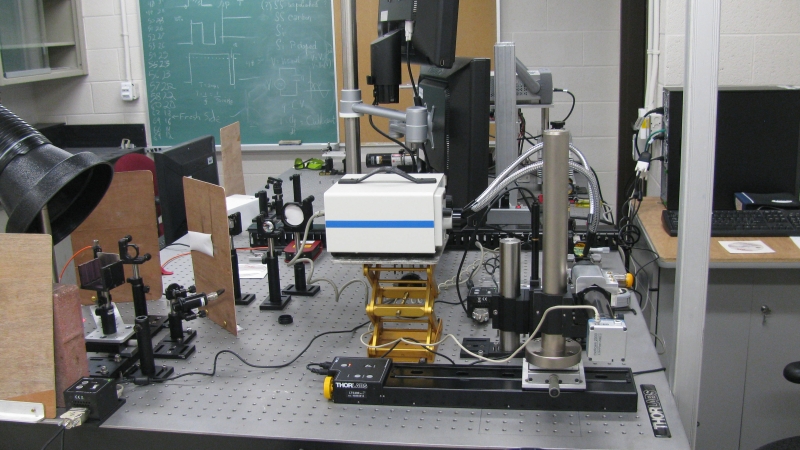
Voici quelques photos des montages sur les tables optiques dans un de mes laboratoires.

Publications et Présentations orales récentes
- L. Lévesque, Jean-Marc Noël, Calum Scott. Controlling the temperature of bones using pulsed CO2 lasers: observations and mathematical modeling, Vol. 6, no. 12, pp. 4768-4780 (2015).
- L.Lévesque, Nyquist sampling theorem: understanding the illusion of the spinning wheel pictured with a video camera, Physics Education; 49(6) pp 697-705 (2014).
- L. Lévesque, Law of cooling, heat conduction and Stefan-Boltzmann radiation laws fitted to experimental data for bones irradiated by CO2 laser, Biomedical Optics Express, Vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 701-712 (2014).
- L. Lévesque, Temperature control of water-based substances by CO2 laser for medical applications, Applied Optics, Vol. 52, no. 16, pp. 3856-3863 (2013).
- L. Lévesque, Reflection, Transmission and Diffraction Efficiencies in Homogeneous Optical Thin Film and Grating Structures: An Overview, Applied Physics Research; Vol. 5, No. 5, pp. 1-20 (2013).
- L. Lévesque, Transfer function of multi-stage active filter: A solution based on Pascal’s triangle, Eur. J. Phys., Vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 55-63 (2012).
- L. Lévesque, R.G. Sabat, Thermal lensing investigation on bulk ceramics and thin-film PLZT using visible and far-infrared laser beams, Opt. Mat., 33, pp. 460-465 (2011).
- L. Lévesque, V. Jdanov, CO2 laser ablation of bent optical fibers for sensing applications, J. Opt. 13, (IOP Publishing), pp. 1-6 (2011).
- L. Lévesque, Determination of thickness and optical constants of metal films from an extended ATR spectrum by using a statistical method, Optics & Laser Technology, 43, pp. 14-19 (2011).
- L. Lévesque, V. Jdanov, Optical fiber cleaved at an angle by CO2 laser ablation: Application to micromachining. Optics & Laser Technology 42, pp. 1080-1083 (2010).
- L. Lévesque, Close up of monochromatic aberration using Snell’s law: an undergraduate computational experiment, Eur. J. of Phys. (IOP Publishing), 30, pp. 1201-1215 (2009).
- L. Lévesque, Divergence of far-infrared laser beam and collimation for Galilean and Keplerian system designs, Optics & Laser Technology, 41, pp. 557-561 (2009).
- L. Lévesque, Simple smoothing technique to reduce data scattering in Physics experiments, Eur. J. Phys. (IOP), 29,155-162, 2008.
- P.L. Rochon et Luc Lévesque, Standing wave surface Plasmon mediated forward and backward scattering, Opt. Express, 14, 13050-13055 (2006).
- P. Rochon, L. Levesque. Multiple surface gratings on azopolymers for generating surface plasmons. Photonics North, Quebec, juin 2006.
- L.Lévesque, P.Rochon. Controlling the photonic bandgap by surface relief azopolymer films sputtered with gold. Canadian Association of Physicists Congress, Brock University, St. Catherine, Ontario, juin 2006.
- L.Lévesque, P.Rochon. Surface plasmon photonic band gap in azopolymer gratings sputtered with gold. JOSA A 22, 2564-2568 (2005).
- L. Lévesque. Revisiting the coupled-mass system and analogy with a simple band gap structure. European Journal of Physics (IOP), 27,133-145 (2006).
- A. Cournoyer, M. Levesque, L.Lévesque. Method for engraving materials using laser etched v-grooves. US Patent no. 7,023,001 (2006).
- P. Rochon, L. Levesque. The use of relief gratings to control and observe surface plasmon propagation. Canadian Association of Physicists Congress, Vancouver, Columie-Britannique, June 2005.
- A. Cournoyer, L.Lévesque, M.Levesque, Sub-spot size CO2 laser micromachining of features in fused silica by V-groove etching, SPIE 5578D, Photonics North, Ottawa, 5578-72, sept. 2004.
- A. Cournoyer, D. Antonov, L.Lévesque, D. Cantin, M. Levesque, Laser drilling and routing in optical fibers and tapered micro-pipettes using excimer, femtosecond and CO2 lasers, SPIE 5578D, Photonics North, Ottawa, 5578-79, sept. 2004.
- M.Levesque, A.Cournoyer, L.Lévesque, CO2 laser processing of optical fibers, Rapports du Congrès 23eme, International Congress on Applications of Lasers and Electro-Optics 2004.
- L.Lévesque, Revisiting the Nyquist Criterion and Aliasing in Data Analysis, Eur. J. Phys. 22 (2001), 127-132.
Livre ou chapitre d’un livre
- L.Lévesque, Cours à distance, Université Laurentienne: Uses of Lasers and Fibers Optics in Medical Sciences (2000). Manuel révisé en 2010.
- L.Lévesque, Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves in Thin Dielectric and Metallic Films (22 pages), Chapitre 12, Electromagnetic Waves, Mars 2011, Volume 1 (INTECH), ISBN 978-953-307-568-6, Edité par Prof. Vitaliy Zhurbenko.
Commentaires
Commentaires et suggestions sont bienvenus à : bryce.bennett@rmc-cmr.ca
